Hacking, malware and social engineering attacks – these are the top three threats for cyber security, according to Verizon’s 2016 Data Breach Investigations Report.
Social engineering attacks are different from hacking and malware, which can be prevented with security solutions that protect against this sort of threat. These types of attacks don’t target an unpatched security bug for example, they target people. Because in the end, the weakest link is the person sitting in front of the computer and... why hack a sophisticated security solution when you can "hack" a human?
The infographic below presents the 5 most common social engineering attack types and explains which industries are most susceptible to this sort of attack.
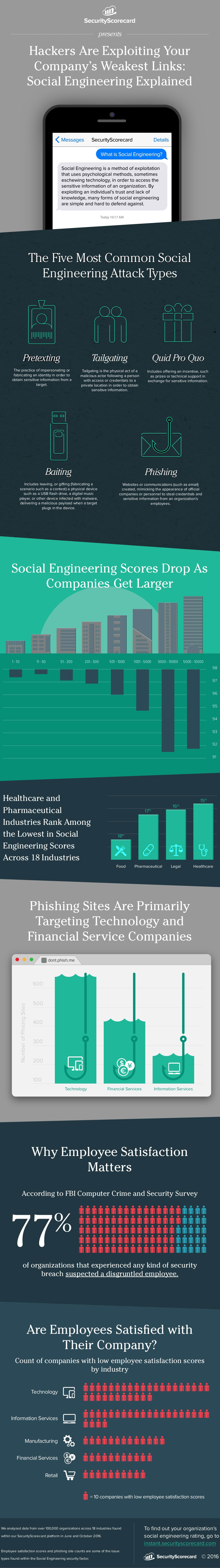
Via SecurityScorecard, company that provides the most accurate security ratings & continuous risk monitoring for vendor and third party risk management.
The 5 Most Common Social Engineering Attack Types
In related news…
Here’s one more infographic, one that presents the 3 main types of social engineering attacks.
Social engineering attacks are different from hacking and malware, which can be prevented with security solutions that protect against this sort of threat. These types of attacks don’t target an unpatched security bug for example, they target people. Because in the end, the weakest link is the person sitting in front of the computer and... why hack a sophisticated security solution when you can "hack" a human?
The infographic below presents the 5 most common social engineering attack types and explains which industries are most susceptible to this sort of attack.

Via SecurityScorecard, company that provides the most accurate security ratings & continuous risk monitoring for vendor and third party risk management.
The 5 Most Common Social Engineering Attack Types
- Pretexting – the practice of impersonating or fabricating an identity in order to obtain sensitive information from a target.
- Tailgating – the physical act of a malicious actor following a person with access or credentials to a private location in order to obtain sensitive information.
- Quid Pro Quo – includes offering an incentive, such as prizes or technical support in exchange for sensitive information.
- Baiting – includes leaving, or gifting (fabricating a scenario such as a contest) a physical device such as a USB flash drive, a digital music player, or other device infected with malware, delivering a malicious payload when a target plugs in the device.
- Phishing – websites or communications (such as email) created, mimicking the appearance of official companies or personnel to steal credentials and sensitive information from an organization’s employees.
In related news…
Here’s one more infographic, one that presents the 3 main types of social engineering attacks.

























