#1 Trojan Guide in 2022
Trojan viruses consistently rank within the top three of the most prevalent and dangerous types of malware each year. Therefore, learning about trojans and understanding how they do damage is paramount to protecting yourself and your equipment from cyber threats.
The following article is designed to provide you with a complete overview of the Trojan virus. In the end, you’ll know how to protect your devices and get rid of trojans for good.
What is a Trojan?
A Trojan virus (named after the Greek myth) is a type of malware that poses as legit software.
Trojans are disguised as a software patch, Word doc, mp4 video, or another harmless file. But, in reality, its purpose is to harm your device or steal data through other forms of malware, such as ransomware, rootkits, backdoors, or spyware. These malicious programs often carry different payloads, so the damage they can cause differs.
Take ransomware, for example. This type of malware attacks and encrypts your data, and, just as its name suggests, the only way to get your data back is to pay a ransom to the hackers. Conversely, a spyware app might run silently in the background, stealing your usernames and passwords. The amount of damage a Trojan can cause is endless.
Even though a Trojan is often referred to as a Trojan virus, this wording is technically incorrect. A virus is a specific kind of malware that can replicate and spread to other systems or programs. Regardless, the term “virus” is still the preferred terminology when discussing malware (malicious software) in general. So, in reality, a Trojan virus means Trojan malware.
Trojans can deliver multiple types of malware, such as ransomware, rootkits, backdoors, or spyware.
Statistics
According to Malwarebytes’ 2021 State of Malware Report, Trojans were the second most detected threat against consumers and the #1 most detected threat against businesses in 2020.
Trojans were the second most detected threat against consumers in 2020.
For consumers, although the Trojan threat count in 2020 is down by 13% since 2019, the numbers are still astronomical — over 23 million.
Source: Malwarebytes’ 2021 State of Malware Report
Regarding businesses, although the number of detected Trojans in 2020 decreased by a staggering 45% compared to the previous year, still, the threat count remained massive — 6.1 million to be precise!
Source: Malwarebytes’ 2021 State of Malware Report
According to Cofense, the notorious Trojan, Emotet, spread malware to 290,000 email addresses in 2019 using 33,000 unique attachments. Emotet was reportedly Malwarebytes’ second most-detected threat against organizations in 2019; however, its spread decreased dramatically in 2020.
Source: Malwarebytes’ 2021 State of Malware Report
Here’s another eye-opening statistic from Statista: malware, which includes trojans, was the most concerning type of cyberthreat according to IT security decision-makers worldwide as of April 2021.
Source: Statista
How do Trojans infect a device?
Source: Heimdal Security
Trojans can infect your computer in several ways. Social engineering is a popular method that cybercriminals use to deliver Trojans. Here’s how it works: a hacker impersonates a well-known company and sends you an email telling you there’s a problem with your account.
Often, the hacker will include a message instructing you to click on a link to fix the issue. That link sends you to a fake website where you’re prompted to enter your personal information — or download some form of malware. Unless you have strong trojan removal software to protect you from phishing emails, there’s a good chance you’ll lose something private and confidential, like your banking credentials.
Another common way to unknowingly contract a Trojan is by visiting suspicious websites, like illegal torrenting platforms or porn sites. You can also pick up a Trojan by installing pirated software, free apps, or screensavers from untrustworthy websites. Malware can even be disguised as patches for fixing hardware and software issues.
Trojan removal software helps you protect private and confidential data.
How harmful are Trojans?
Trojans come in many forms and can cause various issues. Here’s a list of the most common types of Trojans and the problems they can cause:
Backdoor — This kind of Trojan creates a “backdoor” into your computer, allowing other forms of malware to access your device without your knowledge. This is the type of Trojan that’s used to initiate a botnet attack. With a Backdoor Trojan, hackers can alter your data, send or receive files, and even alter your computer settings via a remote access tool (RAT).
Banker Trojans — Hackers use these Trojans to steal your online banking credentials, including usernames, passwords, and credit card numbers. The famous Trojan, Emotet, responsible for a massive email-led cyber attack in 2019, started as a banking Trojan before evolving into something more complex.
Exploit — These malicious programs take advantage of a vulnerability in a target operating system or application. They often pose as patches that promise to fix existing vulnerabilities.
Rootkit — A rootkit allows other forms of malware to hide in plain sight on your device by disguising them as essential files. A rootkit can even be activated before an OS boots up, making it extremely difficult to detect and remove.
DDoS Trojan — These Trojans perform a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack on targeted websites. Once it infects multiple computers, this kind of Trojan will force said computers to access a particular website. Consequently, this floods the website’s server with additional traffic to the point where users can’t access it.
Downloader Trojan — This form of malware can download and install other malicious software onto your device. In short, it infects an already infected computer even more. Emotet was also an example of a downloader Trojan as it infiltrated unsuspecting devices via phishing and downloaded additional forms of malware, including ransomware.
Ransom Trojan — If your computer/mobile device is infected with this form of malware, then your files are at risk of being hijacked. If this happens, the cybercriminals responsible won’t release your files unless you pay the ransom.
Dropper Trojan — Hackers use this malicious software to install Trojan horses or to prevent malware detection. As some antivirus solutions are not equipped to detect Dropper Trojans, they often remain free to carry out their sinister purposes.
Fake AV Trojan — These are Trojans that mimic legitimate antivirus solutions. Essentially, they create bogus malware detections and demand money from their target to eliminate the supposed threat.
GameThief Trojan — As its name suggests, this software is used to steal usernames and passwords from gamers.
IM Trojan — This malware can obtain an unsuspecting user’s account information from instant messaging apps, such as Skype, WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and more.
SMS Trojan — This type of Trojan infects your mobile phone, causing it to send text messages to premium-rate numbers.
Spy Trojan — This type of Trojan acts like spyware, silently running in the background logging your keystrokes, taking screenshots, and intercepting other personal information.
Mailfinder Trojan — This specialized Trojan harvests email addresses from your contacts.
Google the programs you don’t recognize to make sure they’re not Trojans.
Trojans on mobile devices
Given that billions of mobile devices are in use today, it’s no wonder that Trojans have found a way to infiltrate them, too. Both Android and iOS devices are frequent targets of Trojan attacks (although the latter has more robust protection features).
Android Trojans tend to come attached to seemingly legit apps and unleash their payloads once an app has been installed. However, these “legit” apps are often pirated, coming from unofficial app stores. Always be careful what apps you download!
Apps that contain malware can steal sensitive data from your devices, such as contacts, SMS texts, and even login credentials. Another way hackers can benefit from iPhone trojans or Android trojans is by sending premium SMS texts, which generate revenue for them.
Both Android and iOS devices are frequent targets of Trojan attacks.
Google Play sometimes detects Trojan-infected apps before it releases them to the public. However, some Trojanized apps could bypass Google Play’s filters, but Google removed the phone Trojan from the store after publication.
iPhone users can relax a little more than Android users — but not completely. Even though the App Store’s safety policies are strict, security experts discovered Trojan malware in 17 App Store applications. This is a testament to just how tricky some cyber crooks can be; it also highlights the importance of a robust iOS antivirus solution. Another way that corrupt apps can infect your iPhone is by installing unofficial software when jailbreaking your phone.
Trojan prevention tips
Follow these practical tips to prevent trojan viruses from infecting your computer or mobile device:
Get an effective anti-trojan solution. Get a good antivirus program like Norton. These critical programs are your first line of defense against Trojan threats in all forms.
Update your software. Keep your operating system and software programs up-to-date, both on Windows and macOS. Software patches often include essential security updates against vulnerabilities.
Use strong passwords. To guard against Trojans that install spyware like keyloggers, be sure to use strong and secure passwords. Avoid using names or dictionary words.
Enable your firewall. A firewall protects your computer and network from unwanted connections. For example, someone might try to access your laptop through an unsecured wi-fi connection. A reliable firewall will protect your network from security breaches.
Exercise caution with emails and websites. Don’t open attachments from suspicious emails to avoid becoming a victim of phishing. For additional security, stay away from unsafe websites such as pirating sites and never click on pop-ups.
Be wary of downloads. Unless you are sure that the file you’ve downloaded is safe, never click on it. Trojans disguise themselves as various file types, such as executables and documents.
Here’s how an antivirus program protects your computer from Trojans:
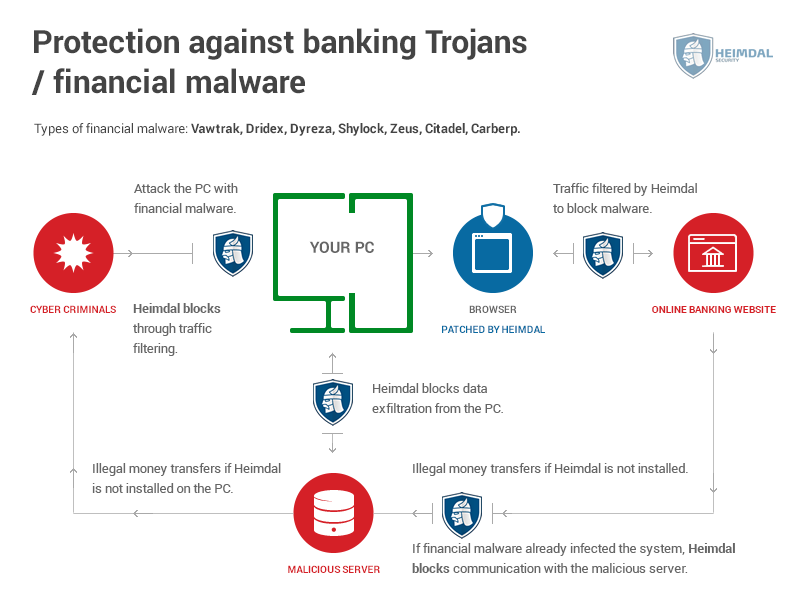
Source: Heimdal Security
Trojan removal tips
A Trojan can be hard to remove once it has infected your device. That’s why some people prefer to wipe out their hard drive if it’s been infected with malware. However, to avoid such a drastic approach and to save time and files (if you don’t have a backup), you’ll be better off using an antivirus program to clean Trojans from your system. Most reputable antivirus software solutions feature versions suitable for all operating systems, both on desktop and mobile.
FAQs about Trojan
What is a Trojan virus?
A Trojan is a type of malware that disguises itself as a legitimate file like an executable or an app. Once a user has installed a corrupted file, the Trojan releases a form of malware into the target device.
This type of malware includes keyloggers, ransomware, backdoor Trojans, and more. A robust anti-trojan antivirus app like Bitdefender can prevent Trojan infections.
Is a Trojan virus dangerous?
Trojans are some of the most dangerous forms of malware out there. They have been responsible for causing billions of dollars worth of damages since their inception in 1975.
For example, the Emotet virus poses a high risk for organizations, costing roughly $1 million per incident to remediate. If organizations and individuals don’t invest in an anti-trojan software solution, they risk Trojan infections and major losses.
Can Trojan viruses be removed?
Yes, most Trojans can be removed once a reputable antivirus software has detected it. However, if you have a backup of your data, simply restore it to remove the Trojan threat.
Where do Trojan viruses come from?
Hackers release Trojan viruses on different areas of the web, such as porn or pirating websites. They also send phishing or spoofing emails to multiple users at once.
For hackers, it’s just a matter of time until someone is fooled into downloading and activating a Trojan. Enhance your internet and email security with an anti-trojan tool to avoid Trojan infections altogether. I’d recommend Bitdefender for its robust malware detection and removal capabilities.
Octav Fedor (Cybersecurity Editor)
Octav is a cybersecurity researcher and writer at AntivirusGuide. When he’s not publishing his honest opinions about security software online, he likes to learn about programming, watch astronomy documentaries, and participate in general knowledge competitions.